 Organizational learning is about growing the intellectual capital of the firm across its people and teams, mobilizing problem-driven, opportunistic and systematic search behaviors.
Organizational learning is about growing the intellectual capital of the firm across its people and teams, mobilizing problem-driven, opportunistic and systematic search behaviors.
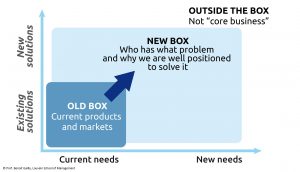 To uncover potential innovation opportunities and foster creativity, organizations and employees need to learn how to generate ideas by thinking in new boxes, challenging their prevailing mental models and “reinventing new wheels”.
To uncover potential innovation opportunities and foster creativity, organizations and employees need to learn how to generate ideas by thinking in new boxes, challenging their prevailing mental models and “reinventing new wheels”.
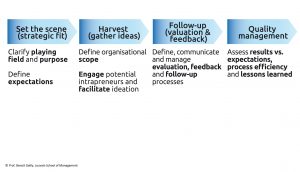 Employees can be a rich source of innovation ideas, provided that goals and expectations as well as coaching, selection, follow-up and feedback processes are carefully managed. Even in the best organizations most ideas end up being rejected. What matters most is what actually does happen the day after the “ideation” events.
Employees can be a rich source of innovation ideas, provided that goals and expectations as well as coaching, selection, follow-up and feedback processes are carefully managed. Even in the best organizations most ideas end up being rejected. What matters most is what actually does happen the day after the “ideation” events.
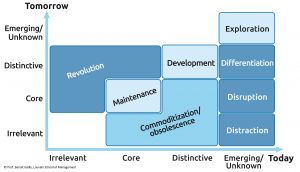 Organizations must decide when and where to build new technology platforms – deploy an R&D strategy – but also how to develop those technology platforms over time in terms of investments, geographic scope and governance – manage R&D operations.
Organizations must decide when and where to build new technology platforms – deploy an R&D strategy – but also how to develop those technology platforms over time in terms of investments, geographic scope and governance – manage R&D operations.
Bibliography
Organizational learning: growing intellectual capital
Keywords: benchmarks, communities of practice, creative industries, double-loop learning, institutional search, intellectual capital, organisational learning, problemistic search, slack, social capital
- (Book) Choo, Chun Wei, and Nick Bontis, eds. The strategic management of intellectual capital and organizational knowledge. Oxford University Press, 2002.
- (Book) Davenport, T. H., Prusak, L. (1998) Working knowledge: How organizations manage what they know, Harvard Business School Press, Boston
- (Book) Greve HR (2003) Organizational Learning from performance feedback: A behavioral perspective on innovation and change; Cambridge University Press, England
- (Book) Lin, N. (2017). Building a network theory of social capital. In Social capital (pp. 3-28). Routledge.
- (Book) Stewart, T. (1997). Intellectual Capital: The New Wealth of Organizations. Doubleday/Currency: New York.
- (Video) How do you define a learning organization? by Peter Senge, Author of The Fifth Discipline
- (Video) The Importance of Learning in Organizations. Harvard Business Review
- (Article) Adams, J. D. (1990). Fundamental stocks of knowledge and productivity growth. Journal of Political Economy, 98(4), 673-702.
- (Article) Adler, P. S., & Kwon, S. W. (2002). Social capital: Prospects for a new concept. Academy of Management Review, 27(1), 17-40.
- (Article) Ahuja, G., & Katila, R. (2004). Where do resources come from? The role of idiosyncratic situations. Strategic Management Journal, 25(8‐9), 887-907.
- (Article) Aloini, D., & Martini, A. (2013). Exploring the exploratory search for innovation: a structural equation modelling test for practices and performance. International Journal of Technology Management 11, 61(1), 23-46.
- (Article) Amin, A., & Roberts, J. (2008). ‘Knowing in action: Beyond communities of practice’. Research Policy, 37, 353-369.
- (Article) Anand, N., Gardner, H. K., & Morris, T. (2007). Knowledge-based innovation: Emergence and embedding of new practice areas in management consulting firms. Academy of Management Journal, 50(2), 406-428.
- (Article) Argote, L., & Miron-Spektor, E. (2011). Organizational learning: From experience to knowledge. Organization Science, 22(5), 1123-1137.
- (Article) Argote, L., Lee, S., & Park, J. (2021). Organizational learning processes and outcomes: Major findings and future research directions. Management Science, 67(9), 5399-5429.
- (Article) Argyris, C. (1976). Single-loop and double-loop models in research on decision making. Administrative Science Quarterly, 363-375.
- (Article) Argyris, C. (1977). Double loop learning in organizations. Harvard Business Review, 55(5), 115-125.
- (Article) Ayas, K., & Zeniuk, N. (2001). Project-based learning: Building communities of reflective practitioners. Management Learning, 32(1), 61-76
- (Article) Bontis, N. (2001) « Assessing knowledge assets: a review of the models used to measure intellectual capital » International Journal of Management Reviews, 3, 1, pp. 41-60
- (Article) Brady, T., & Davies, A. (2004). Building project capabilities: from exploratory to exploitative learning. Organization studies, 25(9), 1601-1621.
- (Article) Brown, J.S., & Duguid, P. (1991). Organizational learning and communities-of-practice: Toward a unified view of working, learning, and innovation. Organization Science, 2(1), 40-57.
- (Article) Brown, J. S., & Duguid, P. (2001). Knowledge and organization: A social-practice perspective. Organization science, 12(2), 198-213.
- (Article) Bueno, E., Aragón, J. A., Paz Salmador, M., & García, V. J. (2010). Tangible slack versus intangible resources: the influence of technology slack and tacit knowledge on the capability of organisational learning to generate innovation and performance. International Journal of Technology Management, 49(4), 314-337.
- (Article) Burt, R. S. (1997). The contingent value of social capital. Administrative Science Quarterly, 339-365.
- (Article) Burt, R. S. (2000). The network structure of social capital. Research in Organizational Behavior, 22, 345-423.
- (Article) Coleman, J. (1988). ‘Social capital in the creation of human capital’. American Journal of Sociology, 94, s95-s120.
- (Article) Cross, R., Parker, A., Prusak, L., & Borgatti, S. P. (2001). Knowing what we know:-supporting knowledge creation and sharing in social networks. Organizational Dynamics, 30(2), 100-120.
- (Article) Crossan, M. M., Lane, H. W., & White, R. E. (1999). An organizational learning framework: From intuition to institution. Academy of Management Review, 24(3), 522-537.
- (Article) Crossan, M. M., & Berdrow, I. (2003). Organizational learning and strategic renewal. Strategic Management Journal, 24(11), 1087-1105.
- (Article) Denrell, J., Fang, C., & Levinthal, D. A. (2004). From T-mazes to labyrinths: Learning from model-based feedback. Management Science, 50(10), 1366-1378.
- (Article) Dost, M., Badir, Y. F., Ali, Z., & Tariq, A. (2016). The impact of intellectual capital on innovation generation and adoption. Journal of Intellectual Capital, 17(4), 675-695.
- (Article) Du, Y., Kim, P. H., Fourné, S. P., & Wang, X. (2022). In times of plenty: Slack resources, R&D investment, and entrepreneurial firms in challenging institutional environments. Journal of Business Research, 145, 360-376.
- (Article) Dunne, D. D., & Dougherty, D. (2016). Abductive reasoning: How innovators navigate in the labyrinth of complex product innovation. Organization Studies, 37(2), 131-159.
- (Article) Edmondson, A.C. (2007). The competitive imperative of learning. Harvard Business Review, 86(7-8), 60-7.
- (Article) Faraj, S., Jarvenpaa, S.L., & Majchrzak, A. (2011). Knowledge collaboration in online communities, Organization Science, 22(5), 1224-1239
- (Article) Fiol, C. M., & Lyles, M. A. (1985). Organizational learning. Academy of Management Review, 10(4), 803-813.
- (Article) Fiol, C. M. (1994). Consensus, diversity, and learning in organizations. Organization Science, 5(3), 403-420.
- (Article) Fong Boh, W., Slaughter, S. A., & Espinosa, J. A. (2007). Learning from experience in software development: A multilevel analysis. Management Science, 53(8), 1315-1331.
- (Article) Garavan, T. N., Carbery, R., & Murphy, E. (2007). Managing intentionally created communities of practice for knowledge sourcing across organisational boundaries: Insights on the role of the CoP manager. The Learning Organization, 14(1), 34-49.
- (Article) Garvin, D. A., Edmondson, A. C., & Gino, F. (2008). Is yours a learning organization?. Harvard Business Review, 86(3), 109.
- (Article) Gavetti, G., & Levinthal, D. (2000). Looking forward and looking backward: Cognitive and experiential search. Administrative Science Quarterly, 45(1), 113-137.
- (Article) Gavetti, G., Greve, H. R., Levinthal, D. A., & Ocasio, W. (2012). The behavioral theory of the firm: Assessment and prospects. The Academy of Management Annals, 6(1), 1-40.
- (Article) Greve, H.R. (2003). A behavioral theory of R&D expenditures and innovations: Evidence from shipbuilding. Academy of Management Journal, 46(6), 685-702.
- (Article) Greve, H. R., & Taylor, A. (2000). Innovations as catalysts for organizational change: Shifts in organizational cognition and search. Administrative Science Quarterly, 45(1), 54-80.
- (Article) Handley, K., Sturdy, A., Fincham, R., & Clark, T. (2006). Within and beyond communities of practice: Making sense of learning through participation, identity and practice. Journal of Management Studies, 43(3), 641-653.
- (Article) Hansen, M. T. (1999). The search-transfer problem: The role of weak ties in sharing knowledge across organization subunits. Administrative Science Quarterly, 44(1), 82-111.
- (Article) Hansen, M. T. (2002). Knowledge networks: Explaining effective knowledge sharing in multiunit companies. Organization Science, 13(3), 232-248.
- (Article) Hansen, M. T., Mors, M. L., & Løvås, B. (2005). Knowledge sharing in organizations: Multiple networks, multiple phases. Academy of Management Journal, 48(5), 776-793.
- (Article) Hatch, N. W., & Dyer, J. H. (2004). Human capital and learning as a source of sustainable competitive advantage. Strategic Management Journal, 25(12), 1155-1178.
- (Article) Hildreth, P., Kimble, C., & Wright, P. (2000). Communities of practice in the distributed international environment. Journal of Knowledge Management, 4(1), 27-38.
- (Article) Holmqvist, M. (2003). A dynamic model of intra-and interorganizational learning. Organization Studies, 24(1), 95-123.
- (Article) Holmqvist, M. (2004). Experiential learning processes of exploitation and exploration within and between organizations: An empirical study of product development. Organization Science, 15(1), 70-81.
- (Article) Hitt, M., Bierman, L., Shimizu, K., & Kochhar, 2. (2001). ‘Direct and moderating effects of human capital on strategy and performance in professional service firms: A resource-based perspective’. Academy of Management Journal, 44, 13-28.
- (Article) Jiménez-Jiménez, D., & Sanz-Valle, R. (2011). Innovation, organizational learning, and performance. Journal of Business Research, 64(4), 408-417.
- (Article) Jung, H. J., & Lee, J. J. (2016). The quest for originality: A new typology of knowledge search and breakthrough inventions. Academy of Management Journal, 59(5), 1725-1753.
- (Article) Katila, R., & Ahuja, G. (2002). Something old, something new: A longitudinal study of search behavior and new product introduction. Academy of Management Journal, 45(6), 1183-1194.
- (Article) Kianto, A., Sáenz, J., & Aramburu, N. (2017). Knowledge-based human resource management practices, intellectual capital and innovation. Journal of Business Research, 81, 11-20.
- (Article) Kneeland, M. K., Schilling, M. A., & Aharonson, B. S. (2020). Exploring uncharted territory: Knowledge search processes in the origination of outlier innovation. Organization Science, 31(3), 535-557.
- (Article) Landry, R., Amara, N., & Lamari, M. (2002). Does social capital determine innovation? To what extent?. Technological forecasting and social change, 69(7), 681-701.
- (Article) Leoncini, R. (2016). Learning-by failing. An empirical exercise on CIS data. Research Policy, 45, 376-386.
- (Article) Lesser, E. L., & Storck, J. (2001). Communities of practice and organizational performance. IBM Systems Journal, 40(4), 831-841.
- (Article) Levinthal, D. A., & March, J. G. (1993). The myopia of learning. Strategic Management Journal, 14(S2), 95-112.
- (Article) Levitt, B., & March, J. G. (1988). Organizational learning. Annual Review of Sociology, 14(1), 319-338.
- (Article) Liu, Y., Lv, D., Ying, Y., Arndt, F., & Wei, J. (2018). Improvisation for innovation: The contingent role of resource and structural factors in explaining innovation capability. Technovation. 74-75, 32-41
- (Article) Malone, D. (2002). Knowledge management: A model for organizational learning. International Journal of Accounting Information Systems, 3(2), 111-123.
- (Article) March, J. G. (1991). Exploration and exploitation in organizational learning. Organization Science, 2(1), 71-87.
- (Article) March, J. G., Sproull, L. S., & Tamuz, M. (1991). Learning from samples of one or fewer. Organization Science, 2(1), 1-13.
- (Article) McDowell, W. C., Peake, W. O., Coder, L., & Harris, M. L. (2018). Building small firm performance through intellectual capital development: Exploring innovation as the “black box”. Journal of Business Research, 88, 321-327.
- (Article) Mittendorff, K., Geijsel, F., Hoeve, A., de Laat, M., & Nieuwenhuis, L. (2006). Communities of practice as stimulating forces for collective learning. Journal of Workplace Learning, 18(5), 298-312.
- (Article) Muthukrishna, M., & Henrich, J. (2016). Innovation in the collective brain. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 371(1690), 20150192.
- (Article) Nahapiet, J., & Ghoshal, S. (1998). Social capital, intellectual capital and the organizational advantage. Academy of Management Review, 23, 242-266.
- (Article) Naldi, L., & Davidsson, P. (2014). Entrepreneurial growth: The role of international knowledge acquisition as moderated by firm age. Journal of Business Venturing, 29(5), 687-703.
- (Article) Nickerson, J. A., & Zenger, T. R. (2004). A knowledge-based theory of the firm—The problem-solving perspective. Organization Science, 15(6), 617-632.
- (Article) Nohria, N., & Gulati, R. (1996). Is slack good or bad for innovation?. Academy of Management Journal, 39(5), 1245-1264.
- (Article) Pattinson, S., & Preece, D. (2014). Communities of practice, knowledge acquisition and innovation: a case study of science-based SMEs. Journal of Knowledge Management, 18(1), 107-120.
- (Article) Pattinson, S., Preece, D., & Dawson, P. (2016). In search of innovative capabilities of communities of practice: A systematic review and typology for future research. Management Learning, 47(5), 506-524.
- (Article) Petty, R., & Guthrie, J. (2000). Intellectual capital literature review: measurement, reporting and management. Journal of Intellectual Capital, 1(2), 155-176.
- (Article) Phelps, C., Heidl, R., & Wadhwa, A. (2012). Knowledge, networks, and knowledge networks: A review and research agenda. Journal of Management, 38(4), 1115-1166.
- (Article) Prencipe, A. (2000). Breadth and depth of technological capabilities in CoPS: the case of the aircraft engine control system. Research Policy, 29(7-8), 895-911.
- (Article) Probst, G., & Borzillo, S. (2008). Why communities of practice succeed and why they fail. European Management Journal, 26(5), 335-347.
- (Article) Roberts, J. (2006). Limits to communities of practice. Journal of Management Studies, 43(3), 623-639.
- (Article) Saban et al. (2000) ‘Organizational learning: A critical component to new product development’, Journal of Product and Brand Management, 9(2), p.101
- (Article) Schilling, J., & Kluge, A. (2009). Barriers to organizational learning: An integration of theory and research. International Journal of Management Reviews, 11(3), 337-360.
- (Article) Schulz, M. (2001). The uncertain relevance of newness: Organizational learning and knowledge flows. Academy of Management Journal, 44(4), 661-681.
- (Article) Sobel, J. (2002). Can we trust social capital?. Journal of Economic Literature, 40(1), 139-154.
- (Article) Stata, R. (1989). Organizational learning-the key to management innovation. MIT Sloan Management Review, 30(3), 63.
- (Article) Subramaniam, M., & Youndt, M.A. (2005). The influence of intellectual capital on the types of innovative capabilities. Academy of Management Journal, 48(3), 450-463.
- (Article) Sussman, S. W., & Siegal, W. S. (2003). Informational influence in organizations: An integrated approach to knowledge adoption. Information Systems Research, 14(1), 47-65.
- (Article) Swan, J., Scarbrough, H., & Robertson, M. (2002). The construction of Communities of Practice in the management of innovation. Management Learning, 33(4), 477-496.
- (Article) Thompson, M. (2005). Structural and epistemic parameters in communities of practice. Organization Science, 16(2), 151-164.
- (Article) Thornhill, S. (2006). Knowledge, innovation and firm performance in high-and low-technology regimes. Journal of Business Venturing, 21(5), 687-703
- (Article) Titus Jr, V., Parker, O., & Covin, J. (2019). Organizational Aspirations and External Venturing: The Contingency of Entrepreneurial Orientation. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 1042258719838473.
- (Article) Uzzi, B., & Lancaster, R. (2003). Relational embeddedness and learning: The case of bank loan managers and their clients. Management Science, 49(4), 383-399.
- (Article) Von Krogh, G., Spaeth, S., & Lakhani, K. R. (2003). Community, joining, and specialization in open source software innovation: a case study. Research policy, 32(7), 1217-1241.
- (Article) Wei, Z., Yi, Y., & Guo, H. (2014). Organizational Learning Ambidexterity, Strategic Flexibility, and New Product Development. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 31(4), 832-847.
- (Article) Wenger, E. C., & Snyder, W. M. (2000) Communities of practice: The organizational frontier. Harvard Business Review, 78(1), 139-146
- (Article) Zhou, J., & George, J. M. (2001). When job dissatisfaction leads to creativity: Encouraging the expression of voice. Academy of Management Journal, 44(4), 682-696.
Idea generation: Thinking in new boxes
Keywords: accommodation, assimilation, association, brainstorming, cognitive dissonance, creativity, framing, gamification, idea generation, lateral thinking, mental models, patterns, problematization, reframing, TRIZ
- (Video) Grant, Adam. The Surprising Habits of Original Thinkers
- (Video) John Cleese on Creativity in Management https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pb5oIIPO62g&ab_channel=VideoArts
- (Book) Alʹtshuller, G. S. (1999). The innovation algorithm: TRIZ, systematic innovation and technical creativity. Technical innovation center, Inc..
- (Book) Amabile, T., & Kramer, S. (2011). The progress principle: Using small wins to ignite joy, engagement, and creativity at work. Harvard Business Press.
- (Book) Amabile, T.M. (1983). The social psychology of creativity. New York: Springer-Verlag;
- (Book) Cabane, O. F., & Pollack, J. (2017). The Net and the Butterfly: The Art and Practice of Breakthrough Thinking. Penguin.
- (Book) Catmull, E. (2008). How Pixar fosters collective creativity. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Publishing
- (Book) Fauconnier, G., & Turner, M. (2008). The way we think: Conceptual blending and the mind’s hidden complexities. Basic Books.
- (Book) Gentner, D., & Stevens, A. L. (Eds.). (2014). Mental models. Psychology Press.
- (Book) Henry, J. (2001). Creativity and perception in management. Sage.
- (Book) Johnson-Laird, P. N. (1983). Mental models: Towards a cognitive science of language, inference, and consciousness (No. 6). Harvard University Press.
- (Book) Kahneman, D. (2011). Thinking, Fast and Slow. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux
- (Book) Kahneman, D., & Tversky, A. (1982). Judgment under Uncertainty: Heuristics and Biases. Cambridge : Cambridge University Press
- (Book) Kelley, T. The art of innovation: Lessons in creativity from IDEO, America’s leading design firm. Vol. 10. Broadway Business, 2001.
- (Video) Creative thinking – how to get out of the box and generate ideas: Giovanni Corazza at TEDxRoma
- (Video) Creativity in the Workplace – Full – Rich Sheridan – Michigan Engineering MconneX
- (Video) Everything is a Remix Part 3 de Kirby Ferguson (on Vimeo)
- (Video) Innovation as a Learning Process by Roger Shealy (on Vimeo)
- (Video) TEDxAtlanta – Teresa Amabile – The Progress Principle
- (Video) Thinking outside the box requires a box: Michael Bahr at TEDxSUU
- (Video) TEDTalk by Luc de Brabandere: Reinventive creative thinking (2015).
- (Video) Creative thinking – how to get out of the box and generate ideas: Giovanni Corazza at TEDxRoma
- (Article) Agogué, M., & Le Masson, P. (2015). Rethinking ideation: a cognitive approach of innovation lock-ins. Academy of Management Proceedings, 2015(1), 15303.
- (Article) Amabile, T. M. (1982). Social psychology of creativity: A consensual assessment technique. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 43(5), 997.
- (Article) Amabile, T. M. (1983). The social psychology of creativity: A componential conceptualization. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 45(2), 357.
- (Article) Amabile, T. M. (1985). Motivation and creativity: Effects of motivational orientation on creative writers. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 48(2), 393.
- (Article) Amabile, T. M., Barsade, S. G., Mueller, J. S., & Staw, B. M. (2005). Affect and creativity at work. Administrative Science Quarterly, 50(3), 367-403.
- (Article) Amabile, T. M., & Pratt, M. G. (2016). The dynamic componential model of creativity and innovation in organizations: Making progress, making meaning. Research in Organizational Behavior, 36, 157-183.
- (Article) Azoulay, P., Fons-Rosen, C., & Zivin, J. S. G. (2019). Does science advance one funeral at a time?. American Economic Review, 109(8), 2889-2920.
- (Article) Baron, R. A. (2006). Opportunity recognition as pattern recognition: How entrepreneurs “connect the dots” to identify new business opportunities. Academy of Management Perspectives, 20(1), 104-119.
- (Article) Barron, F., & Harrington, D. M. (1981). Creativity, intelligence, and personality. Annual Review of Psychology, 32(1), 439-476.
- (Article) Battilana, J., Leca, B., & Boxenbaum, E. (2009). 2 how actors change institutions: towards a theory of institutional entrepreneurship. Academy of Management Annals, 3(1), 65-107.
- (Article) Bell, A., Chetty, R., Jaravel, X., Petkova, N., & Van Reenen, J. (2019). Who becomes an inventor in America? The importance of exposure to innovation. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 134(2), 647-713.
- (Article) Berg, J. M. (2014). The primal mark: How the beginning shapes the end in the development of creative ideas. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 125(1), 1-17.
- (Article) Bessant, J., Von Stamm, B., Moeslein, K. M., & Neyer, A. K. (2010). Backing outsiders: selection strategies for discontinuous innovation. R&D Management, 40(4), 345-356.
- (Article) Björk, J., Boccardelli, P., & Magnusson, M. (2010). Ideation capabilities for continuous innovation. Creativity and Innovation Management, 19(4), 385-396.
- (Article) Bledow, R., Rosing, K., & Frese, M. (2013). A dynamic perspective on affect and creativity. Academy of Management Journal, 56(2), 432-450.
- (Article) Bloom, N., Jones, C. I., Van Reenen, J., & Webb, M. (2020). Are ideas getting harder to find?. American Economic Review, 110(4), 1104-44.
- (Article) Boland Jr, R. J., & Tenkasi, R. V. (1995). Perspective making and perspective taking in communities of knowing. Organization Science, 6(4), 350-372.
- (Article) Brem, A., Puente-Diaz, R., & Agogué, M. (2016). Creativity and innovation: State of the art and future perspectives for research. International Journal of Innovation Management, 20(04), 1602001.
- (Article) Castillo-Vergara, M., Alvarez-Marin, A., & Placencio-Hidalgo, D. (2018). A bibliometric analysis of creativity in the field of business economics. Journal of Business Research, 85, 1-9.
- (Article) Dane, E. (2010). Reconsidering the trade-off between expertise and flexibility: A cognitive entrenchment perspective. Academy of Management Review, 35(4), 579-603.
- (Article) Davis, M. A. (2009). Understanding the relationship between mood and creativity: A meta-analysis. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 108(1), 25-38.
- (Article) Dean, D. L., Hender, J., Rodgers, T., & Santanen, E. (2006). Identifying good ideas: constructs and scales for idea evaluation. Journal of Association for Information Systems, 7(10), 646-699.
- (Article) Diehl, M., & Stroebe, W. (1987). Productivity loss in brainstorming groups: Toward the solution of a riddle. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 53(3), 497-509.
- (Article) Eppler, M. J., Hoffmann, F., & Bresciani, S. (2011). New business models through collaborative idea generation. International Journal of Innovation Management, 15(06), 1323-1341.
- (Article) Feist, G. J. (1998). A meta-analysis of personality in scientific and artistic creativity. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 2(4), 290-309.
- (Article) Fleming, L., & Sorenson, O. (2001). Technology as a complex adaptive system: evidence from patent data. Research Policy, 30(7), 1019-1039.
- (Article) Fong, C. T. (2006). The effects of emotional ambivalence on creativity. Academy of Management Journal, 49(5), 1016-1030.
- (Article) Gallupe, R. B., Dennis, A. R., Cooper, W. H., Valacich, J. S., Bastianutti, L. M., & Nunamaker Jr, J. F. (1992). Electronic brainstorming and group size. Academy of Management Journal, 35(2), 350-369.
- (Article) Gassmann, O., & Zeschky, M. (2008). Opening up the solution space: the role of analogical thinking for breakthrough product innovation. Creativity and Innovation Management, 17(2), 97-106.
- (Article) George, J. M. (2007). Creativity in organizations. The Academy of Management Annals, 1(1), 439-477.
- (Article) George, J. M., & Zhou, J. (2001). When openness to experience and conscientiousness are related to creative behavior: an interactional approach. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86(3), 513.
- (Article) George, J. M., & Zhou, J. (2007). Dual tuning in a supportive context: Joint contributions of positive mood, negative mood, and supervisory behaviors to employee creativity. Academy of Management Journal, 50(3), 605-622.
- (Article) Gilbert, C. G. (2006). Change in the presence of residual fit: Can competing frames coexist?. Organization Science, 17(1), 150-167.
- (Article) Gioia, D. A., Schultz, M., & Corley, K. G. (2000). Organizational identity, image, and adaptive instability. Academy of Management Review, 25(1), 63-81.
- (Article) Girotra, K., Terwiesch, C., & Ulrich, K. T. (2010). Idea generation and the quality of the best idea. Management Science, 56(4), 591-605.
- (Article) Grant, A. M., & Berry, J. W. (2011). The necessity of others is the mother of invention: Intrinsic and prosocial motivations, perspective taking, and creativity. Academy of Management Journal, 54(1), 73-96.
- (Article) Grégoire, D. A., Barr, P. S., & Shepherd, D. A. (2010). Cognitive processes of opportunity recognition: The role of structural alignment. Organization Science, 21(2), 413-431.
- (Article) Grilli, L., & Pedota, M. (2024). Creativity and artificial intelligence: A multilevel perspective. Creativity and Innovation Management. 1-14
- (Article) Gruber, M., MacMillan, I. C., & Thompson, J. D. (2013). Escaping the prior knowledge corridor: What shapes the number and variety of market opportunities identified before market entry of technology start-ups?. Organization Science, 24(1), 280-300.
- (Article) Hargadon, A., & Sutton, R. I. (1997). Technology brokering and innovation in a product development firm. Administrative Science Quarterly, 716-749.
- (Article) Hennessey BA, Amabile TM. 2010. Creativity. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 61:569–98
- (Article) Hodgkinson, G. P., Bown, N. J., Maule, A. J., Glaister, K. W., & Pearman, A. D. (1999). Breaking the frame: An analysis of strategic cognition and decision making under uncertainty. Strategic Management Journal, 977-985.
- (Article) Jansson, D.G., and Smith, S.M. (1991). Design fixation, Design Studies, 12 (1), 3-11.
- (Article) Kahneman, D. (2003). Maps of bounded rationality: Psychology for behavioral economics. The American Economic Review, 93(5), 1449-1475.
- (Article) Kaplan, S. (2008). Framing contests: Strategy making under uncertainty. Organization Science, 19(5), 729-752.
- (Article) Kavadias, S., & Sommer, S. C. (2009). The effects of problem structure and team diversity on brainstorming effectiveness. Management Science, 55(12), 1899-1913.
- (Article) Kilgour, M., & Koslow, S. (2009). Why and how do creative thinking techniques work?: Trading off originality and appropriateness to make more creative advertising. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 37(3), 298-309.
- (Article) Kim, K. H. (2006). Can we trust creativity tests? A review of the Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking (TTCT). Creativity Research Journal, 18(1), 3-14.
- (Article) King, L. A., Walker, L. M., & Broyles, S. J. (1996). Creativity and the five-factor model. Journal of Research in Personality, 30(2), 189-203.
- (Article) Liao, S., Fei, W., & Liu, C. (2008). Relationships between knowledge inertia, organizational learning and organizational innovation. Technovation, 28, 183-195.
- (Article) Maguire, S., & Hardy, C. (2009). Discourse and deinstitutionalization: The decline of DDT. Academy of Management Journal, 52(1), 148-178.
- (Article) Malik, M. A. R., & Butt, A. N. (2017). Rewards and Creativity: Past, Present, and Future. Applied Psychology, 66(2), 290-325.
- (Article) Mednick, Sarnoff. “The associative basis of the creative process.” Psychological Review, 69.3 (1962): 220.
- (Article) Mumford, M. D. (2003). Where have we been, where are we going? Taking stock in creativity research. Creativity Research Journal, 15(2-3), 107-120.
- (Article) Oldham, G. R., & Da Silva, N. (2015). The impact of digital technology on the generation and implementation of creative ideas in the workplace. Computers in Human Behavior, 42, 5-11.
- (Article) Paulus, P. B., & Yang, H. C. (2000). Idea generation in groups: A basis for creativity in organizations. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 82(1), 76-87.
- (Article) Perry-Smith, J. E., & Shalley, C. E. (2003). The social side of creativity: A static and dynamic social network perspective. Academy of Management Review, 28(1), 89-106.
- (Article) Petruzzelli, A. M., & Savino, T. (2014). Search, recombination, and innovation: Lessons from haute cuisine. Long Range Planning, 47(4), 224-238.
- (Article) Poskela, J., & Martinsuo, M. (2009). Management control and strategic renewal in the front end of innovation. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 26(6), 671-684.
- (Article) Roth, S., Schneckenberg, D., & Tsai, C. W. (2015). The ludic drive as innovation driver: Introduction to the gamification of innovation. Creativity and Innovation Management, 24(2), 300-306.
- (Article) Runco, M. A., & Jaeger, G. J. (2012). The standard definition of creativity. Creativity Research Journal, 24(1), 92-96.
- (Article) Savino, T., Messeni Petruzzelli, A., & Albino, V. (2017). Search and recombination process to innovate: a review of the empirical evidence and a research agenda. International Journal of Management Reviews, 19(1), 54-75.
- (Article) Shalley, C. E., Gilson, L. L., & Blum, T. C. (2009). Interactive effects of growth need strength, work context, and job complexity on self-reported creative performance. Academy of Management Journal, 52(3), 489-505.
- (Article) Sosa, M. E. (2011). Where do creative interactions come from? The role of tie content and social networks. Organization Science, 22(1), 1-21.
- (Article) Sternberg, R. J. (2006). The nature of creativity. Creativity Research Journal, 18(1), 87.
- (Article) Sutton, R. I., & Hargadon, A. (1996). Brainstorming groups in context: Effectiveness in a product design firm. Administrative Science Quarterly, 685-718.
- (Article) Teodoridis, F., Bikard, M., & Vakili, K. (2019). Creativity at the knowledge frontier: The impact of specialization in fast-and slow-paced domains. Administrative Science Quarterly, 64(4), 894-927.
- (Article) Tripsas, M., & Gavetti, G. (2000). Capabilities, cognition, and inertia: Evidence from digital imaging. Strategic Management Journal, 21(10‐11), 1147-1161.
- (Article) Unsworth, K. (2001). Unpacking creativity. Academy of Management Review, 26(2), 289-297.
- (Article) Walsh, J. P. (1995). Managerial and organizational cognition: Notes from a trip down memory lane. Organization Science, 6(3), 280-321.
- (Article) Ward, T., Patterson, M. J., & Sifonis, C. M. (2004). The role of specificity and abstraction in creative idea generation. Creativity Research Journal, 16(1), pp. 1-9.
- (Article) Wedell-Wedellsborg, T. (2017). Are you solving the right problems. Harvard Business Review, 95(1), 76-83.
- (Article) Woodman, R. W., Sawyer, J. E., & Griffin, R. W. (1993). Toward a theory of organizational creativity. Academy of Management Review, 18(2), 293-321.
Fostering employee-driven innovation
Keywords: business plan competition, challenges, employee-driven innovation, idea boxes, ideation, slack search
- (Book) Høyrup, S. (2012) Employee-driven innovation: a new phenomenon, concept and mode of innovation. Palgrave Macmillan UK.
- (Book) Patterson, F., Port, R. L., and Hobley, S. (2003) The Psychology of Innovation and Creativity: A review of research and practice in organisations. Chartered Institute of Personal Development. ISBN 0-9545861-0-7.
- (Video) Fostering creativity and innovation in the workplace: Jude Reggett at TEDxNorthernSydneyInstitute
- (Article) Artto, K., Kulvik, I., Poskela, J., & Turkulainen, V. (2011). The integrative role of the project management office in the front end of innovation. International Journal of Project Management, 29(4), 408-421.
- (Article) Axtell, C. M., Holman, D. J., Unsworth, K. L., Wall, T. D., Waterson, P. E., & Harrington, E. (2000). Shopfloor innovation: Facilitating the suggestion and implementation of ideas. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 73(3), 265-285
- (Article) Bernstein, B., & Singh, P. J. (2006). An integrated innovation process model based on practices of Australian biotechnology firms. Technovation, 26(5-6), 561-572.
- (Article) Bessant, J., & Caffyn, S. (1997). High-involvement innovation through continuous improvement. International Journal of Technology Management, 14(1), 7-28.
- (Article) Bessant, J., Caffyn, S., & Gallagher, M. (2001). An evolutionary model of continuous improvement behaviour. Technovation, 21(2), 67-77.
- (Article) Bharadwaj, S., & Menon, A. (2000). Making innovation happen in organizations: individual creativity mechanisms, organizational creativity mechanisms or both?. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 17(6), 424-434.
- (Article) Bjelland, O. M., & Wood, R. C. (2008). An inside view of IBM’s’ Innovation Jam’. MIT Sloan Management Review, 50(1), 32.
- (Article) Carrier, C. (1998). Employee creativity and suggestion programs: an empirical study. Creativity and Innovation Management, 7(2), 62-72.
- (Article) Chen, J., Leung, W. S., & Evans, K. P. (2016). Are employee-friendly workplaces conducive to innovation?. Journal of Corporate Finance, 40, 61-79.
- (Article) Cornelius, P. B., Gokpinar, B., & Sting, F. J. (2021). Sparking manufacturing innovation: How temporary interplant assignments increase employee idea values. Management Science, 67(4), 2231-2250.
- (Article) Fairbank, J. F., & Williams, S. D. (2001). Motivating creativity and enhancing innovation through employee suggestion system technology. Creativity and Innovation Management, 10(2), 68-74.
- (Article) Gray, P., Parise, S., & Iyer, B. (2011). ‘Innovation Impacts of Using Social Bookmarking Systems’. MIS Quarterly, 35, 629-643.
- (Article) Isaksen, S. G., & Ekvall, G. (2010). Managing for innovation: The two faces of tension in creative climates. Creativity and Innovation Management, 19(2), 73-88.
- (Article) Kesting, P., & Parm Ulhøi, J. (2010). Employee-driven innovation: extending the license to foster innovation. Management Decision, 48(1), 65-84.
- (Article) Mainemelis, C. (2010). Stealing fire: Creative deviance in the evolution of new ideas. Academy of Management Review, 35(4), 558-578.
- (Article) Martinez, M. (2015). Solver engagement in knowledge sharing in crowdsourcing communities: Exploring the link to creativity. Research Policy, 44, 1419-1430.
- (Article) Martinsuo, M. (2009). Teaching the fuzzy front end of innovation: experimenting with team learning and cross‐organizational integration. Creativity and Innovation Management, 18(3), 147-159.
- (Article) Mumford, M. D. (2000). Managing creative people: Strategies and tactics for innovation. Human Resource Management Review, 10(3), 313-351.
- (Article) Nelson, B. A., Wilson, J. O., Rosen, D., & Yen, J. (2009). Refined metrics for measuring ideation effectiveness. Design Studies, 30(6), 737-743.
- (Article) Rhee, L., & Leonardi, P. M. (2018). Which pathway to good ideas? A n attention‐based view of innovation in social networks. Strategic Management Journal, 39(4), 1188-1215.
- (Article) Rigtering, J. C., Weitzel, G. U., & Muehlfeld, K. K. (2018). Increasing quantity without compromising quality: How managerial framing affects intrapreneurship. Journal of Business Venturing, 34(2), 224-241.
- (Article) Shah, J. J., Smith, S. M., & Vargas-Hernandez, N. (2003). Metrics for measuring ideation effectiveness. Design Studies, 24(2), 111-134.
- (Article) Siggelkow, N., & Rivkin, J. W. (2006). When exploration backfires: Unintended consequences of multilevel organizational search. Academy of Management Journal, 49(4), 779-795.
- (Article) Tierney, P., & Farmer, S. M. (2002). Creative self-efficacy: Its potential antecedents and relationship to creative performance. Academy of Management Journal, 45(6), 1137-1148.
- (Article) Toubia, O. (2006). Idea generation, creativity, and incentives. Marketing Science, 25(5), 411-425.
- (Article) Van Dijk, C., & Van Den Ende, J. (2002). Suggestion systems: transferring employee creativity into practicable ideas. R&D Management, 32(5), 387-395.
- (Article) Wallace, J. C., Butts, M. M., Johnson, P. D., Stevens, F. G., & Smith, M. B. (2016). A multilevel model of employee innovation: Understanding the effects of regulatory focus, thriving, and employee involvement climate. Journal of Management, 42(4), 982-1004.
Developing new technology platforms
Keywords: R&D definition, R&D expenditures, R&D location, R&D management, R&D performance, technology platforms
- (Book) Kuhn, T. (2014). What are scientific revolutions?. Philosophy, Science, and History: A Guide and Reader, 71.
- (Video) Disruptive Innovation Festival by James Curran (on Vimeo)
- (Video) Inventing the Impossible: Pablos Holman at TEDxUCSD
- (Article) Almeida, P., & Phene, A. (2004). Subsidiaries and knowledge creation: The influence of the MNC and host country on innovation. Strategic Management Journal, 25(8‐9), 847-864.
- (Article) Argyres, N. S., & Silverman, B. S. (2004). R&D, organization structure, and the development of corporate technological knowledge. Strategic Management Journal, 25(8‐9), 929-958.
- (Article) Asakawa, K. (2001). Organizational tension in international R&D management: the case of Japanese firms. Research Policy, 30(5), 735-757.
- (Article) Augsdorfer, P. (2005). Bootlegging and path dependency. Research Policy, 34(1), 1-11.
- (Article) Bremser, W. G., & Barsky, N. P. (2004). Utilizing the balanced scorecard for R&D performance measurement. R&D Management, 34(3), 229-238.
- (Article) Breschi, S., Lissoni, F., & Malerba, F. (2003). Knowledge-relatedness in firm technological diversification. Research Policy, 32(1), 69-87.
- (Article) Brynjolfsson, Erik, and Lorin M. Hitt. (2000) “Beyond computation: Information technology, organizational transformation and business performance.” The Journal of Economic Perspectives 14.4 (2000): 23-48.
- (Article) Cardinal, L. B. (2001). Technological innovation in the pharmaceutical industry: The use of organizational control in managing research and development. Organization Science, 12(1), 19-36.
- (Article) Cesaroni, F., Minin, A. D., & Piccaluga, A. (2005). Exploration and exploitation strategies in industrial R&D. Creativity and Innovation Management, 14(3), 222-232.
- (Article) Chen, C. J., Huang, Y. F., & Lin, B. W. (2012). How firms innovate through R&D internationalization? An S-curve hypothesis. Research Policy, 41(9), 1544-1554.
- (Article) Cohen, W., & Levinthal, D. (1989). ‘Innovation and learning: The two faces of R&D’. Econom. Journal, 99, 569-596.
- (Article) Dattée, B., Alexy, O., & Autio, E. (2018). Maneuvering in poor visibility: How firms play the ecosystem game when uncertainty is high. Academy of Management Journal, 61(2), 466-498.
- (Article) DeSanctis, G., Glass, J. T., & Ensing, I. M. (2002). Organizational designs for R&D. Academy of Management Perspectives, 16(3), 55-66.
- (Article) Feinberg, S. E., & Gupta, A. K. (2004). Knowledge spillovers and the assignment of R&D responsibilities to foreign subsidiaries. Strategic Management Journal, 25(8‐9), 823-845.
- (Article) Galunic, D. C., & Rodan, S. (1998). Resource recombinations in the firm: Knowledge structures and the potential for Schumpeterian innovation. Strategic Management Journal, 19(12), 1193-1201.
- (Article) Helfat, C. E. (1997). Know‐how and asset complementarity and dynamic capability accumulation: the case of R&D. Strategic Management Journal, 18(5), 339-360.
- (Article) Henttonen, K., Ojanen, V., & Puumalainen, K. (2016). Searching for appropriate performance measures for innovation and development projects. R&D Management, 46(5), 914-927.
- (Article) Higon, D. (2016). In-house versus external basic research and first-to-market innovations. Research Policy, 45, 816-829.
- (Article) Jaffe, A. B., (1986). Technological Opportunity and Spillovers of R&D: Evidence from Firms’ Patents, Profits, and Market Value. The American Economic Review, 76(5), 984-1001.
- (Article) Kaplan, S., Murray, F., & Henderson, R. (2003). Discontinuities and senior management: Assessing the role of recognition in pharmaceutical firm response to biotechnology. Industrial and Corporate Change, 12(2), 203-233.
- (Article) Kapoor, R., & Furr, N.R. (2015). Complementarities and competition: Unpacking the drivers of entrants’ technology choices in the solar photovoltaic industry. Strategic Management Journal, 36(3), 416-436.
- (Article) Kim, D. J., & Kogut, B. (1996). Technological platforms and diversification. Organization Science, 7(3), 283-301.
- (Article) Lahiri, N. (2010). Geographic distribution of R&D activity: how does it affect innovation quality?. Academy of Management Journal, 53(5), 1194-1209.
- (Article) Leiponen, A., & Helfat, C. E. (2011). Location, decentralization, and knowledge sources for innovation. Organization Science, 22(3), 641-658.
- (Article) Leten, B., Belderbos, R., & Van Looy, B. (2007). Technological diversification, coherence, and performance of firms. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 24(6), 567-579.
- (Article) Lin, B. W., & Chen, J. S. (2005). Corporate technology portfolios and R&D performance measures: a study of technology intensive firms. R&D Management, 35(2), 157-170.
- (Article) Nieto, M. J., & Rodriguez, A. (2011). Offshoring of R&D: Looking abroad to improve innovation performance. Journal of International Business Studies, 42(3), 345-361.
- (Article) Oriani, R., & Sobrero, M. (2008). Uncertainty and the market valuation of R&D within a real options logic. Strategic Management Journal, 29(4), 343-361.
- (Article) Pavitt, K. (1984). Sectoral patterns of technical change: towards a taxonomy and a theory. Research Policy, 13(6), 343-373.
- (Article) Pavitt, K. (1990). What we know about the strategic management of technology. California Management Review, 32(3), 17-26.
- (Article) Pistorius, C. W., & Utterback, J. M. (1997). Multi-mode interaction among technologies. Research Policy, 26(1), 67-84.
- (Article) Prahalad, CK, Hamel, G (1990) “The core competencies of the corporation”, HBR May-June, 79-91
- (Article) Reger, G. (2004). Coordinating globally dispersed research centres of excellence—the case of Philips Electronics. Journal of International Management, 10(1), 51-76.
- (Article) Rosenberg, N. (1990). Why do firms do basic research (with their own money)?. Research Policy, 19(2), 165-174.
- (Article) Rotolo, D., Hicks, D., & Martin, B. R. (2015). What is an emerging technology?. Research Policy, 44(10), 1827-1843.
- (Article) Scannell, J.W., Alex Blanckley, Helen Boldon & Brian Warrington (2012) Diagnosing the decline in pharmaceutical R&D efficiency, Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 11, 191-200
- (Article) Shefer, D., & Frenkel, A. (2005). R&D, firm size and innovation: an empirical analysis. Technovation, 25(1), 25-32.
- (Article) Shin, J., Coh, B. Y., & Lee, C. (2013). Robust future‐oriented technology portfolios: Black–Litterman approach. R&D Management, 43(5), 409-419.
- (Article) Singh, J. (2008). Distributed R&D, cross-regional knowledge integration and quality of innovative output. Research Policy, 37(1), 77-96.
- (Article) Steinberg, P. J., Procher, V. D., & Urbig, D. (2017). Too much or too little of R&D offshoring: The impact of captive offshoring and contract offshoring on innovation performance. Research Policy, 46(10), 1810-1823.
- (Article) Suzuki, J., & Kodama, F. (2004). Technological diversity of persistent innovators in Japan: Two case studies of large Japanese firms. Research Policy, 33(3), 531-549.
- (Article) Taylor, A. (2010). The next generation: Technology adoption and integration through internal competition in new product development. Organization Science, 21(1), 23-41.
- (Article) Tsai, W. (2001). ‘Knowledge transfer in intraorganizational networks: effects of network position and absorptive capacity on business unit innovation and performance’. Academy of Management Journal, 44, 996-1004.
- (Article) Von Zedtwitz, M., & Gassmann, O. (2002). Market versus technology drive in R&D internationalization: four different patterns of managing research and development. Research Policy, 31(4), 569-588.
- (Article) Wang, C. H., Lu, I. Y., & Chen, C. B. (2008). Evaluating firm technological innovation capability under uncertainty. Technovation, 28(6), 349-363.
- (Article) Zahra, S. A. (1996). Technology strategy and financial performance: Examining the moderating role of the firm’s competitive environment. Journal of Business Venturing, 11(3), 189-219.
(c) Prof. Benoit Gailly, Louvain School of Management


