NEW: Watch the executive summary
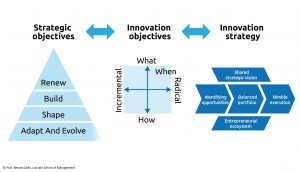
Innovation is a means, not an end per se. A firm’s innovation strategy should be about how its management of innovations will help it to leverage its unique resources and adjust to changes in its environment, in line with its corporate purpose.

Innovation strategies should be based on what the firm understands are the present and future key success factors relevant in the environment it faces, including in particular new partnerships, and its present and future sources of competitive advantages, including in particular its unique datasets.
Innovation strategies should be based on a shared understanding of who are the key stakeholders, including shareholders, employees, customers and society, and what are their expectations, especially regarding the time horizon considered and sustainable levels of ambition.

Strategy should drive innovation, not the other way around. A firm’s innovation posture should therefore be defined based on what its strategic objectives are in terms of innovation, and not just on the latest innovation buzzwords or recipes.
Bibliography
Innovation as a means, not an end
Keywords: drivers of innovation, environment, mission, purpose, resource, SWOT, vision
- (Book) Davila, T., Epstein, M., & Shelton, R. (2012). Making innovation work: How to manage it, measure it, and profit from it. FT press.
- (Video) Fast food nation (Richard Linklater)
- (Video) Unsafe at any speed (Ralph Nader)
- (Video) The Zinnovants “Innovation in tune with your strategy”
- (Article) Beckert, J. (1999). Agency, entrepreneurs, and institutional change. The role of strategic choice and institutionalized practices in organizations. Organization Studies, 20(5), 777-799.
- (Article) Burgelman, R. A. (1983). A model of the interaction of strategic behavior, corporate context, and the concept of strategy. Academy of Management Review, 8(1), 61-70.
- (Article) Child, J. (1997). Strategic choice in the analysis of action, structure, organizations and environment: Retrospect and prospect. Organization Studies, 18(1), 43-76.
- (Article) Cho, H. J., & Pucik, V. (2005). Relationship between innovativeness, quality, growth, profitability, and market value. Strategic Management Journal, 26(6), 555-575.
- (Article) Covin J.G. & Slevin D. P. (1989) Strategic management of small firms in hostile and benign environments. Strategic Management Journal, 10 (January): 75-87.
- (Article) Dobni, C.B. (2010). The relationship between an innovation orientation and competitive strategy. International Journal of Innovation Management, 14(2), 331 – 357.
- (Article) Jayaram, J., Oke, A., & Prajogo, D. (2014). The antecedents and consequences of product and process innovation strategy implementation in Australian manufacturing firms. International Journal of Production Research, 52(15), 4424-4439.
- (Article) Kalay, F., & Lynn, G. (2015). The Impact of Strategic Innovation Management Practices on Firm Innovation Performance. Research Journal of Business and Management, 2(3), 412-429.
- (Article) Mintzberg, H. (1978). Patterns in strategy formation. Management Science, 24(9), 934-948.
- (Article) Prajogo, D. I. (2016). The strategic fit between innovation strategies and business environment in delivering business performance. International Journal of Production Economics, 171, 241-249.
- (Article) Rosenbusch, N., Brinckmann, J., & Bausch, A. (2011). Is innovation always beneficial? A meta-analysis of the relationship between innovation and performance in SMEs. Journal of Business Venturing, 26(4), 441-457.
- (Article) Sirmon, D. G., Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., & Gilbert, B. A. (2011). Resource orchestration to create competitive advantage: Breadth, depth, and life cycle effects. Journal of Management, 37(5), 1390-1412.
- (Article) Wadho, W., & Chaudhry, A. (2018). Innovation and firm performance in developing countries: The case of Pakistani textile and apparel manufacturers. Research Policy, 47(7), 1283-1294.
- (Article) Zajac, E.J., Kraatz, M.S., & Bresser, R.K. (2000). Modeling the dynamics of strategic fit: A normative approach to strategic change. Strategic Management Journal, 429-453.
Key success factors and sources of competitive advantages
Keywords: big data, competitive advantage, corporate resources, external analysis, five-force framework, internal analysis, new entrants, PESTEL, Porter’s framework, resource-based view.
- (Book) Shapiro, C., Carl, S., & Varian, H. R. (1998). Information rules: a strategic guide to the network economy. Harvard Business Press.
- (Book) Vullings, R., & Heleven, M. (2016). Not Invented Here”, CrossIndustry Innovation, Carl Hanser Verlag GmbH Co KG
- (Video) Stephen Shapiro’s Innovation Philosophy
- (Article) Acedo, F. J., Barroso, C., & Galan, J. L. (2006). The resource‐based theory: dissemination and main trends. Strategic Management Journal, 27(7), 621-636.
- (Article) Adner, R., & Helfat, C. E. (2003). Corporate effects and dynamic managerial capabilities. Strategic Management Journal, 24(10), 1011-1025.
- (Article) Barney, J. B. (1986). Strategic factor markets: Expectations, luck, and business strategy. Management Science, 32(10), 1231-1241.
- (Article) Barney, J. (1991). ‘Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage’. Journal of Management, 17, 99-120.
- (Article) Barney, J. B. (2001). Resource-based theories of competitive advantage: A ten-year retrospective on the resource-based view. Journal of Management, 27(6), 643-650.
- (Article) Black, J. A., & Boal, K. B. (1994). Strategic resources: Traits, configurations and paths to sustainable competitive advantage. Strategic Management Journal, 15(S2), 131-148.
- (Article) Chen, H., Chiang, R. H., & Storey, V. C. (2012). Business intelligence and analytics: From big data to big impact. MIS quarterly, 36(4).
- (Article) Danneels, E. (2002). The dynamics of product innovation and firm competences. Strategic Management Journal, 23(12), 1095-1121.
- (Article) Denrell, J., Fang, C., & Zhao, Z. (2013). Inferring superior capabilities from sustained superior performance: A Bayesian analysis. Strategic Management Journal, 34(2), 182-196.
- (Article) Dougherty, D., & Dunne, D. D. (2011). Organizing ecologies of complex innovation. Organization Science, 22(5), 1214-1223.
- (Article) Furr, N., & Kapoor, R. (2017). Capabilities, technologies, and firm exit during industry shakeout: Evidence from the global solar photovoltaic industry. Strategic Management Journal.
- (Article) Granstrand, O., Patel, P., & Pavitt, K. (1997). Multi-technology corporations: why they have “distributed” rather than “distinctive core” competencies. California Management Review, 39(4), 8-25.
- (Article) Hall, R. (1993). A framework linking intangible resources and capabiliites to sustainable competitive advantage. Strategic Management Journal, 14(8), 607-618.
- (Article) Henderson, R., & Cockburn, I. (1994). Measuring competence? Exploring firm effects in pharmaceutical research. Strategic Management Journal, 15(S1), 63-84.
- (Article) Henderson, R., & Mitchell, W. (1997). The interactions of organizational and competitive influences on strategy and performance. Strategic Management Journal, 18(S1), 5-14.
- (Article) Hoopes, D. G., Madsen, T. L., & Walker, G. (2003). Guest editors’ introduction to the special issue: why is there a resource‐based view? Toward a theory of competitive heterogeneity. Strategic Management Journal, 24(10), 889-902.
- (Article) Klenner, P., Hüsig, S., & Dowling, M. (2013). Ex-ante evaluation of disruptive susceptibility in established value networks—When are markets ready for disruptive innovations?. Research Policy, 42(4), 914-927.
- (Article) Leavy, B. (2003). Assessing your strategic alternatives from both a market position and core competence perspective. Strategy & Leadership, 31(6), 29-35.
- (Article) Lewin, A. Y., Long, C. P., & Carroll, T. N. (1999). The coevolution of new organizational forms. Organization Science, 10(5), 535-550.
- (Article) Li, H., & Atuahene-Gima, K. (2001). Product innovation strategy and the performance of new technology ventures in China. Academy of Management Journal, 44(6), 1123-1134.
- (Article) Liao, J. J., Kickul, J. R., & Ma, H. (2009). Organizational dynamic capability and innovation: An empirical examination of internet firms. Journal of Small Business Management, 47(3), 263-286.
- (Article) Makadok, R. (2001). Toward a synthesis of the resource‐based and dynamic‐capability views of rent creation. Strategic Management Journal, 22(5), 387-401.
- (Article) Markides, C. C., & Williamson, P. J. (1996). Corporate diversification and organizational structure: A resource-based view. Academy of Management Journal, 39(2), 340-367.
- (Article) Nalebuff , B.J. Adam M. Brandenburger, (1997),”Co-opetition: Competitive and cooperative business strategies for the digital economy”, Strategy & Leadership, 25(6), 28 – 33
- (Article) Oliver, Ch. (1997). Sustainable competitive advantage: Combining institutional and resource-based views. Strategic Management Journal, 697-713.
- (Article) Parmar, R., Mackenzie, I., Cohn, D., & Gann, D. (2014). The new patterns of innovation. Harvard Business Review, 92(1), 2.
- (Article) Patel, P., & Pavitt, K. (1997). The technological competencies of the world’s largest firms: complex and path-dependent, but not much variety. Research Policy, 26(2), 141-156.
- (Article) Peteraf, M. A. (1993). The cornerstones of competitive advantage: A resource‐based view. Strategic Management Journal, 14(3), 179-191.
- (Article) Porter, M. 1996. What is Strategy? Harvard Business Review: 61-78
- (Article) Ray, G., Barney, J. B., & Muhanna, W. A. (2004). Capabilities, business processes, and competitive advantage: choosing the dependent variable in empirical tests of the resource‐based view. Strategic Management Journal, 25(1), 23-37.
- (Article) Saebi, T., Lien, L., & Foss, N. J. (2017). What drives business model adaptation? The impact of opportunities, threats and strategic orientation. Long range planning, 50(5), 567-581.
- (Article) Salancik, G. R., & Meindl, J. R. (1984). Corporate attributions as strategic illusions of management control. Administrative Science Quarterly, 238-254.
- (Article) Schreyögg, G., & Kliesch‐Eberl, M. (2007). How dynamic can organizational capabilities be? Towards a dual‐process model of capability dynamization. Strategic Management Journal, 28(9), 913-933.
- (Article) Simpson, D. G. (1998). Why most strategic planning is a waste of time and what you can do about it. Long Range Planning, 31(3), 476-480.
- (Article) Sirmon, D. G., Hitt, M. A., & Ireland, R. D. (2007). Managing firm resources in dynamic environments to create value: Looking inside the black box. Academy of Management Review, 32(1), 273-292.
- (Article) Thornhill, S., & Amit, R. (2003). Learning about failure: Bankruptcy, firm age, and the resource-based view. Organization Science, 14(5), 497-509.
- (Article) Tripsas, M. (1997). Unraveling the process of creative destruction: Complementary assets and incumbent survival in the typesetter industry. Strategic Management Journal, 18(S1), 119-142.
- (Article) Uzunca, B. (2018). A Competence-Based View of Industry Evolution: The Impact of Submarket Convergence on Incumbent− Entrant Dynamics. Academy of Management Journal, 61(2), 738-768.
- (Article) Wamba, S. F., Gunasekaran, A., Akter, S., Ren, S. J. F., Dubey, R., & Childe, S. J. (2017). Big data analytics and firm performance: Effects of dynamic capabilities. Journal of Business Research, 70, 356-365.
- (Article) Wernerfelt, B. (1984). A resource‐based view of the firm. Strategic Management Journal, 5(2), 171-180.
- (Article) Winter, S. (2003). ‘Understanding dynamic capabilities’. Strategic Management Journal, 24, 991-995.
- (Article) Yoffie, D. B., & Kwak, M. (2006). With friends like these: The art of managing complementors. Harvard Business Review, 84(9), 88-98
- (Article) Zahra, S. A. (1993). Environment, corporate entrepreneurship, and financial performance: A taxonomic approach. Journal of Business Venturing, 8(4), 319-340.
- (Article) Zahra, S. A. (1996). Goverance, ownership, and corporate entrepreneurship: The moderating impact of industry technological opportunities. Academy of Management Journal, 39(6), 1713-1735.
- (Article) Zollo, M., & Winter, S.G. (2002). Deliberate learning and the evolution of dynamic capabilities. Organization Science, 13(3): 339-351.
Purpose: managing stakeholder expectations
Keywords: business ethics, corporate purpose, expectation management, KPI, Luddites, responsible innovation, shareholders and stakeholder, strategic horizons
- (Book) Baghai, M., Coley, S., & White, D. (2000). The alchemy of growth: Practical insights for building the enduring enterprise. Da Capo Press.
- (Book) Jonas, H. (1985). The imperative of responsibility: In search of an ethics for the technological age. University of Chicago press.
- (Book) Pavie, X. (2012). Innovation-responsable: stratégie et levier de croissance des organisations. Editions Eyrolles.
- (Video) The Zinnovants “Why innovate?”
- (Article) Ahlstrom, D. (2010). Innovation and growth: How business contributes to society. Academy of Management Perspectives, 24(3), 11-24.
- (Article) Austin, J., Stevenson, H., & Wei‐Skillern, J. (2006). Social and commercial entrepreneurship: same, different, or both?. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 30(1), 1-22.
- (Article) Bowen, F. E., Rostami, M., & Steel, P. (2010). Timing is everything: A meta-analysis of the relationships between organizational performance and innovation. Journal of Business Research, 63(11), 1179-1185.
- (Article) Camillus, J. C. (2008). Strategy as a wicked problem. Harvard Business Review, 86(5), 98.
- (Article) Clarke, T. (1998). The stakeholder corporation: A business philosophy for the information age. Long Range Planning, 31(2), 182-194.
- (Article) Eccles, R. G., Ioannou, I., & Serafeim, G. (2014). The impact of corporate sustainability on organizational processes and performance. Management Science, 60(11), 2835-2857.
- (Article) Flammer, C., & Bansal, P. (2017). Does a long‐term orientation create value? Evidence from a regression discontinuity. Strategic Management Journal, 38(9), 1827-1847.
- (Article) Frey, C. B., & Osborne, M. A. (2017). The future of employment: how susceptible are jobs to computerisation?. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 114, 254-280.
- (Article) Gobble, M. M. (2015). The case against disruptive innovation. Research-Technology Management, 58(1), 59-63.
- (Article) Gottschalg, O., & Zollo, M. (2007). Interest alignment and competitive advantage. Academy of Management Review, 32(2), 418-437.
- (Article) Greenwood, R., Raynard, M., Kodeih, F., Micelotta, E. R., & Lounsbury, M. (2011). Institutional complexity and organizational responses. Academy of Management Annals, 5(1), 317-371.
- (Article) Hitt, M.A., Ireland, R.D., Sirmon, D.G., & Trahms, C.A. (2011). Strategic entrepreneurship: creating value for individuals, organizations, and society. The Academy of Management Perspectives, 25(2), 57-75.
- (Article) Hoskisson, R. E., Hitt, M. A., Johnson, R. A., & Grossman, W. (2002). Conflicting voices: The effects of institutional ownership heterogeneity and internal governance on corporate innovation strategies. Academy of Management Journal, 45(4), 697-716.
- (Article) Kock, C. J., Santaló, J., & Diestre, L. (2012). Corporate governance and the environment: what type of governance creates greener companies?. Journal of Management Studies, 49(3), 492-514.
- (Article) Lehman, D. W., O’Connor, K., Kovács, B., & Newman, G. E. (2019). Authenticity. Academy of Management Annals, 13(1), 1-42.
- (Article) Leiponen, A. & Helfat, C.E. (2010). Innovation objectives, knowledge sources, and the benefits of breadth. Strategic Management Journal, 31, 224–236.
- (Article) Martinez-Conesa, I., Soto-Acosta, P., & Palacios-Manzano, M. (2017). Corporate social responsibility and its effect on innovation and firm performance: An empirical research in SMEs. Journal of Cleaner Production, 142, 2374-2383.
- (Article) Pache, A. C., & Santos, F. (2010). When worlds collide: The internal dynamics of organizational responses to conflicting institutional demands. Academy of Management Review, 35(3), 455-476.
- (Article) Pache, A. C., & Santos, F. (2013). Inside the hybrid organization: Selective coupling as a response to competing institutional logics. Academy of Management Journal, 56(4), 972-1001.
- (Article) Rubera, G., & Kirca, A. H. (2012). Firm innovativeness and its performance outcomes: A meta-analytic review and theoretical integration. Journal of Marketing, 76(3), 130-147.
- (Article) Sitkin, S. B., See, K. E., Miller, C. C., Lawless, M. W., & Carton, A. M. (2011). The paradox of stretch goals: Organizations in pursuit of the seemingly impossible. Academy of Management Review, 36(3), 544-566.
- (Article) Stilgoe, J., Owen, R., & Macnaghten, P (2013). Developing a framework for responsible innovation. Research Policy, 42(9), 1568-1580.
Define your innovation posture
Keywords: configuration, innovation strategy, strategic choices
- (Book) Freeman (1988) The Economics of Industrial Innovation. Cambridge MA: MIT Press
- (Book) Miles, R.E. and Snow, C.C. (1978). Organizational strategy, structure, and process. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- (Video) The Importance of an Innovation Strategy by Kuczmarski Innovation (on Vimeo)
- (Article) Aragón‐Sánchez, A., & Sánchez‐Marín, G. (2005). Strategic orientation, management characteristics, and performance: A study of Spanish SMEs. Journal of Small Business Management, 43(3), 287-308.
- (Article) Atuahene-Gima, K., & Ko, A. (2001). An empirical investigation of the effect of market orientation and entrepreneurship orientation alignment on product innovation. Organization Science, 12(1), 54-74.
- (Article) Avermaete, T., Viaene, J., Morgan, E. J., & Crawford, N. (2003). Determinants of innovation in small food firms. European Journal of Innovation Management, 6(1), 8-17.
- (Article) Azar, G., & Ciabuschi, F. (2017). Organizational innovation, technological innovation, and export performance: The effects of innovation radicalness and extensiveness. International Business Review, 26(2), 324-336.
- (Article) Becheikh, N., Landry, R., & Amara, N. (2006). Lessons from innovation empirical studies in the manufacturing sector: A systematic review of the literature from 1993–2003. Technovation, 26(5-6), 644-664.
- (Article) Damanpour, F., Szabat, K. A., & Evan, W. M. (1989). The relationship between types of innovation and organizational performance. The Journal of Management Studies, 26(6), 587.
- (Article) Damanpour, F., & Wischnevsky, J. D. (2006). Research on innovation in organizations: Distinguishing innovation-generating from innovation-adopting organizations. Journal of Engineering and Technology Management, 23(4), 269-291.
- (Article) Danneels, E. (2008). Organizational antecedents of second‐order competences. Strategic Management Journal, 29(5), 519-543.
- (Article) De Jong, J. P., & Marsili, O. (2006). The fruit flies of innovations: A taxonomy of innovative small firms. Research Policy, 35(2), 213-229.
- (Article) De Massis, A., Audretsch, D., Uhlaner, L., & Kammerlander, N. (2018). Innovation with Limited Resources: Management Lessons from the German Mittelstand. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 35(1), 125-146.
- (Article) DeSarbo, W.S., Benedetto, C.A.D., Song, M. and Sinha, I. (2005). Revisiting the Miles and Snow strategic framework. Strategic Management Journal, 26(1), 47-74
- (Article) Dibrell, C., Craig, J. B., & Neubaum, D. O. (2014). Linking the formal strategic planning process, planning flexibility, and innovativeness to firm performance. Journal of Business Research, 67(9), 2000-2007.
- (Article) Du, J., Love, J. H., & Roper, S. (2007). The innovation decision: An economic analysis. Technovation, 27(12), 766-773.
- (Article) Fiss, P. C. (2011). Building better causal theories: A fuzzy set approach to typologies in organization research. Academy of Management Journal, 54(2), 393-420.
- (Article) Ganter, A., & Hecker, A. (2014). Configurational paths to organizational innovation: qualitative comparative analyses of antecedents and contingencies. Journal of Business Research, 67(6), 1285-1292.
- (Article) Gatignon, H., & Xuereb, J. M. (1997). Strategic orientation of the firm and new product performance. Journal of Marketing Research, 77-90.
- (Article) Gimenez, F. A. (2000). The benefits of a coherent strategy for innovation and corporate change: a study applying Miles and Snow’s model in the context of small firms. Creativity and Innovation Management, 9(4), 235-244.
- (Article) Gunday, G., Ulusoy, G., Kilic, K., & Alpkan, L. (2011). Effects of innovation types on firm performance. International Journal of Production Economics, 133(2), 662-676.
- (Article) Hall, L. A., & Bagchi-Sen, S. (2007). An analysis of firm-level innovation strategies in the US biotechnology industry. Technovation, 27(1-2), 4-14.
- (Article) Hobday, M., Rush, H., & Bessant, J. (2004). Approaching the innovation frontier in Korea: the transition phase to leadership. Research Policy, 33(10), 1433-1457.
- (Article) Hollenstein, H. (2003). Innovation modes in the Swiss service sector: a cluster analysis based on firm-level data. Research Policy, 32(5), 845-863.
- (Article) Iyer, B., & Davenport, T. H. (2008). Reverse engineering Google’s innovation machine. Harvard Business Review, 86(4), 58-68
- (Article) Kanter, R. M. (2006). Innovation: The classic traps. Harvard Business Review, 84(11), 72-83.
- (Article) Knight, G. A., & Cavusgil, S. T. (2004). Innovation, organizational capabilities, and the born-global firm. Journal of International Business Studies, 35(2), 124-141.
- (Article) Kötting, M., & Kuckertz, A. (2019). Three configurations of corporate innovation programs and their interplay. European Journal of Innovation Management.
- (Article) Laosirihongthong, T., Prajogo, D. I., & Adebanjo, D. (2014). The relationships between firm’s strategy, resources and innovation performance: resources-based view perspective. Production Planning & Control, 25(15), 1231-1246.
- (Article) Lightfoot, H. W., & Gebauer, H. (2011). Exploring the alignment between service strategy and service innovation. Journal of Service Management, 22(5), 664-683.
- (Article) Linton, G., & Kask, J. (2017). Configurations of entrepreneurial orientation and competitive strategy for high performance. Journal of Business Research, 70, 168-176.
- (Article) Loewe, P., Williamson, P., & Wood, R. C. (2001). Five styles of strategy innovation and how to use them. European Management Journal, 19(2), 115-125.
- (Article) Miller, D., & Friesen, P. (1982). ‘Innovation in conservative and entrepreneurial firms: two models of strategic momentum’. Strategic Management Journal, 3, 1-24.
- (Article) Mintzberg, H. (1994). The fall and rise of strategic planning. Harvard Business Review, 72(1), 107-114.
- (Article) Naranjo-Valencia, J., Jiménez-Jiménez, D., & Sanz-Valle, R. (2011). ‘Innovation or imitation? The role of organizational culture’. Management Decision, 49, 55-72.
- (Article) Olson, E.M., Slater, S.F. and Hult, G.T.M. (2005). The performance implications of fit among business strategy, marketing organization structure, and strategic behaviour. Journal of Marketing, 69(3), 49-65.
- (Article) Ortt, J. R., & van der Duin, P. A. (2008). The evolution of innovation management towards contextual innovation. European Journal of Innovation Management, 11(4), 522-538.
- (Article) Pérez-Luño, A., Wiklund, J., & Cabrera, R.V. (2011). The dual nature of innovative activity: How entrepreneurial orientation influences innovation generation and adoption. Journal of Business Venturing, 26(5), 555-571.
- (Article) Pisano, G.P. (2015). You need an innovation strategy. Harvard Business Review, 93(6), 44-54.
- (Article) Prange, C., & Schlegelmilch, B. B. (2018). Managing innovation dilemmas: The cube solution. Business Horizons, 61(2), 309-322.
- (Article) Reeves, M., Love, C., & Tillmanns, P. (2012). Your strategy needs a strategy. Harvard Business Review, 90(9), 76-83.
- (Article) Roberts, P. W., & Amit, R. (2003). The dynamics of innovative activity and competitive advantage: The case of Australian retail banking, 1981 to 1995. Organization Science, 14(2), 107-122.
- (Article) Srholec, M., & Verspagen, B. (2012). The Voyage of the Beagle into innovation: explorations on heterogeneity, selection, and sectors. Industrial and Corporate Change, 21(5), 1221-1253.
- (Article) Tether, B., & Tajar, A. (2008). ‘The organisational-cooperation mode of innovation and its prominence amongst European service firms’. Research Policy, 37, 720-739.
- (Article) Walker, R. M. (2008). An empirical evaluation of innovation types and organizational and environmental characteristics: Towards a configuration framework. Journal of Public Administration Research and Theory, 18(4), 591-615.
- (Article) Zahra, S. A., & Covin, J. G. (1995). Contextual influences on the corporate entrepreneurship-performance relationship: A longitudinal analysis. Journal of Business Venturing, 10(1), 43-58.
(c) Prof. Benoit Gailly, Louvain School of Management


